Nipah Virus
Explore this page for Nipah Virus information, resources, and news.
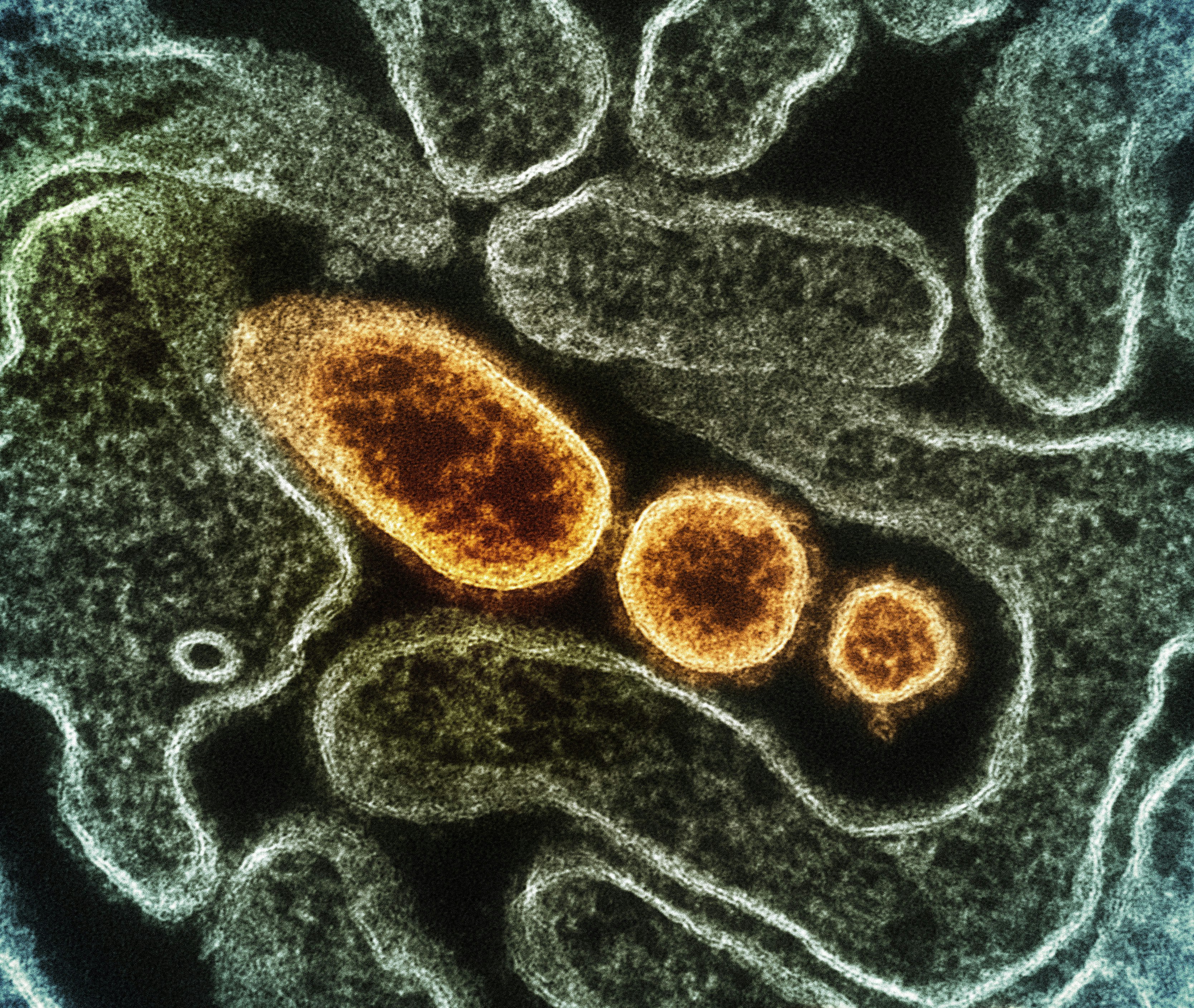
About Nipah Virus
Nipah virus (NiV) is a highly contagious, zoonotic virus (it spreads from animals to humans) that causes severe disease in humans, including acute respiratory illness and fatal encephalitis (brain inflammation).Nipah virus is an RNA virus belonging to the Henipavirus genus in the Paramyxoviridae family. It is classified as a biosafety level-4 pathogen due to its high mortality rate and lack of specific antiviral treatment.
What to know:
- Symptoms typically appear 4–14 days after exposure and may include fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, sore throat, dizziness, confusion, altered consciousness and seizures and coma in severe cases.
- Fruit bats (Pteropus species) are the natural reservoir.
- Humans can get infected through direct contact with infected bats or pigs, eating food contaminated by bat saliva or urine (e.g., raw date palm sap), or Human-to-human transmission, especially in healthcare or household setting.
- Nipah virus outbreaks have only been reported in Bangladesh, India, Malaysia, Philippines, and Singapore. However, the fruit bats that carry the virus can be found throughout Asia, the South Pacific, and Australia.
- February 2, 2026: The CDC is currently monitoring the Nipah virus outbreak in India. Read more here: CDC monitoring deadly Nipah virus outbreak in India