Do you:
- consider what might go wrong in a situation and how you might prevent it from happening or minimize the effects?
- have backup airway equipment and vasopressors available for an anesthesia case?
- check the winter weather before traveling and adjust your travel route or departure time if there are icy roads forecasted?
If you answered “yes” to any of those examples, you are practicing FMEA.
Do you:
- reflect on and identify the causes if you are unable to start an IV, intubate a patient, or are late to work?
- identify and work on how you might prevent the same problem(s) in the future?
If you answered “yes,” you are practicing RCA.
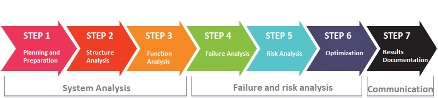
FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
- Looks forward; proactive
- Identifies and addresses potential problems or failures
- Effective with new and existing processes
- Identifies potential pitfalls and unintended consequences of new processes
- Identifies how proposed changes will impact the system
- Improves product and process reliability, quality, and safety
- Begun in the 1940s in the US military
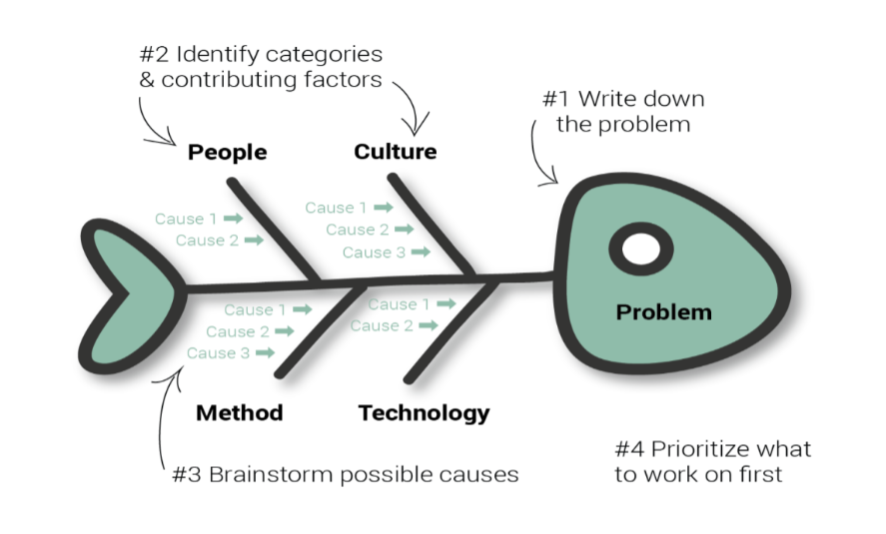
RCA: Root Cause Analysis
- Looks backward to develop actions
- Investigates adverse events, near misses
- Identifies system breakdowns and what contributed to an event
- Identifies what needs to be changed to prevent recurrence of event or near miss
- Reduces risk to the overall organization
- Developed by manufacturing in 1950s
Basic summary of steps utilized by performance improvement teams:
| FMEA | RCA |
| Select a process for analysis | Identify the event to be investigated |
| Identify team members involved in or affected by the process | Identify team members with knowledge of the event |
| Describe the process in detail | Describe what happened |
| Identify what could go wrong during each step of the process | Identify all contributing factors |
| Select which problems to work on eliminating | Analyze contributing factors; Identify root causes |
| Design and implement changes to reduce or prevent problems from occurring | Design and implement changes to eliminate root causes |
| Monitor and measure the success of process changes | Monitor and measure the success of improvement actions |
References:
- https://www.cms.gov
- https://www.ihi.org
- Senders, JW. FMEA and RCA: the mantras of modern risk management. 10.1136/qshc.2004.010868;www.qshc.com. Downloaded from http://qualitysafety.bmj.com